Learning requirements
1.2 Students will recognize the components and organization of
systems and the interconnections within and among them.
1.3 Students will understand that interactions in the physical
environment may cause changes in matter and energy.
2.2 Students will apply science knowledge and skills to solve
problems or meet challenges.
3.2 Students will know that science and technology are human
endeavors, interrelated to each other, to society, and to the
workplace.
Grade Levels
6th-10th grades
Subjects
Earth science and geomorphology
Concept
Erosion and deposition
Skills
Observation, inference, and measurement
Objective
Students will learn to identify landforms caused by erosion and
deposition.
Time Needed
1 to 3 hours
Adapted from EARTH CONNECTIONS Resources For Teaching Earth Science
Permission is granted to photocopy this lesson. There is no copyright.
Mudpile Mountain
The erosion of a mountain by water can be demonstrated by pouring water on a mudpile. This makes it easy for students, even in flat country, to get a better understanding of mountains, their erosional and depositional landforms, and the processes that form them. This outdoor lesson plan is good for groups of any size. Students will construct a ‘mountain’ of dirt, pour water over it, and identify landforms caused by erosion and deposition.Caution students not to carry the comparison of mountain to mudpile too far. Mountains are not just piles of dirt but consist chiefly of bedrock. The bedrock is weathered and transported in several different ways and not just simply eroded away by water.
Erosion and Deposition
Weathering breaks up rocks, but what process carries the pieces away? Erosion. It breaks down the Earth’s crust and carries away the pieces to deposit them elsewhere. The three main agents of erosion are water, ice, and wind.Running water (rivers and streams) is the most common agent of erosion. Glaciers, immense sheets of moving ice, slowly grind away and carry off large chunks of the Earth’s crust. The wind carries sand and dust, which act like sandpaper to wear down the rocks it contacts.
Erosional landforms illustrated by this activity include streams, canyons, and waterfalls. Depositional landforms illustrated include alluvial fans and deltas. This exercise also demonstrates the selective transport of materials by water. Fine particles are carried farther than coarse particles. Fast-moving water carries heavier particles than slowmoving water.
Glossary
Discuss the new vocabulary before starting the activity:
alluvium – silt, sand, clay, gravel, and other loose rock material deposited by flowing water,
as in a riverbed or delta.
alluvial fan – the fan-shaped deposit of alluvium left by a stream where it issues from a
canyon onto a plain.
bedrock – the solid rock underlying the soil and other loose rock material on the Earth’s
surface.
canyon – a narrow valley with steep walls, formed by running water.
delta – a triangular alluvial deposit formed where a river enters a large body of water.
deposition – the laying down of material carried by water
erosion – the wearing away of the soil and rock of the Earth’s crust
landforms – any physical, recognizable form or feature of the Earth’s surface having a
characteristic shape and produced by natural causes. Examples include mountains, valleys,
deltas, and canyons.
sediment – fragmented rock material, such as silt, sand, clay, gravel, carried and deposited
by water, wind, or ice.
silt – sediment made up of fine mineral particles smaller than sand and larger than clay.
transport – to carry from one place to another.
weathering – the mechanical and chemical processes by which rock exposed to the
weather turns into soil.
Procedure
- Have each student rule lines 1 centimeter apart across both sides of a popsicle stick, starting from one end. Then have them crayon centimeter-wide bands, neatly, in this order: red, green, orange, blue, yellow, and purple.
- Take the class outside to a patch of bare ground and dig up dirt, removing larger pebbles and stones. Dump the dirt in a pile and tamp it down to make a ‘mountain’ about half a meter high.
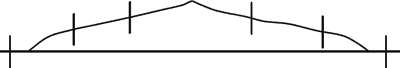
- Have the students push their sticks into the ‘mountain’ and
the surrounding ‘land’, red ends out, so that the sticks are vertical
and evenly distributed. (See drawing below) The boundary
between the orange and blue bands should be even with the
mudpile surface.
- Have one student sprinkle the ‘mountain’ with a watering can so that the ‘rain’ falls straight down. Let everyone in the class have a chance to be the rainmaker, while the others observe and chart the results.
- After the ‘mountain’ is well eroded, ask the following questions:
- Do some markers indicate where erosion is taking place? Where is the material being removed?
- Do some markers indicate where deposition is taking place? Where is dirt being deposited?
- Which of these landforms can you identify: streams, canyons, waterfalls, lakes, deltas, alluvial fans?
- Which is carried farther by the water: sand or silt or rocks? What, if anything, seems to slow erosion on the ‘mountain’?
- Have the students identify as many of the erosional and depositional landforms on the ‘mountain’ as they can.
- Have the students hypothesize why some areas moved at different rates and where the best places to build a house or a waterslide park would be.
- Let the class continue to erode the ‘mountain’ and observe it for several days. Measure and record changes in erosion. Draw pictures each day and record measurements in a table.
- Give extra credit for any photographs of erosional or depositional landforms from magazines or books that are brought to class and correctly identified.