PLATE XX.42
Ancient Work, Liberty Township, Ross County, Ohio.
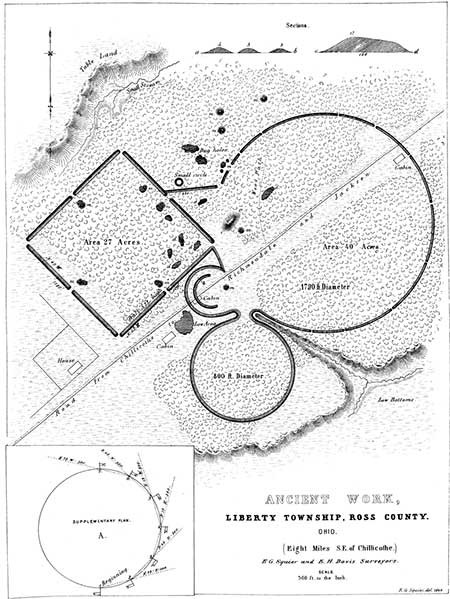 THIS work is a very fair type of a singular series occurring in the Scioto valley,—all
of which have the same figures in combination, although occupying different positions
with respect to each other, viz. a square and two circles. These figures are
not only accurate squares and perfect circles, but are in most cases of corresponding
dimensions,—that is to say, the sides of each of the squares are each ten hundred
and eighty feet in length; and the diameter of each of the large and small circles, a
fraction over seventeen hundred and eight hundred feet, respectively. Such were
the results of surveys made at different times, the measurements of which correspond
within a few feet. Although in the progress of investigation singular coincidences
were observed between these works, yet there was at the time no suspicion of the
identity which subsequent comparison has shown to exist.
THIS work is a very fair type of a singular series occurring in the Scioto valley,—all
of which have the same figures in combination, although occupying different positions
with respect to each other, viz. a square and two circles. These figures are
not only accurate squares and perfect circles, but are in most cases of corresponding
dimensions,—that is to say, the sides of each of the squares are each ten hundred
and eighty feet in length; and the diameter of each of the large and small circles, a
fraction over seventeen hundred and eight hundred feet, respectively. Such were
the results of surveys made at different times, the measurements of which correspond
within a few feet. Although in the progress of investigation singular coincidences
were observed between these works, yet there was at the time no suspicion of the
identity which subsequent comparison has shown to exist.
The first of the series here represented, is situated on the east bank of the Scioto river, and occupies the third bottom or terrace. The ground upon which it occurs is level. The walls of the entire work are unaccompanied by a ditch, and are slight, nowhere more than four feet in height. The embankment of the square is perceptibly heavier than that of the small circle, which is also heavier than that of the larger one. The square work measures ten hundred and eighty feet upon each side; and its walls are interrupted at the corners and at the middle of each side, by gateways thirty feet in width. The central gateways are each covered by a small mound, of about the same height with the embankment, and placed forty feet interior to it. The manner in which the circular works are connected with the square enclosure, and the relative position of each, are accurately shown in the plan, precluding the necessity of a long and intricate description. It will be observed, that while the wall of the larger circle is interrupted by numerous narrow gateways, that of the smaller one is entire throughout,—a feature for which it is, of course, impossible to assign a reason. Besides the small mounds at the gateways, there are three others within the work, two of which are inconsiderable, while the other is of the largest size, being one hundred and sixty feet long, by not far from twenty feet high. A section of this mound is given, illustrative of a detailed description, in a subsequent chapter. There are also a few other mounds outside of the walls, reference to which is had elsewhere. Numerous dug holes occur in the vicinity of the great mound. Most of these are interior to the work,—a very unusual circumstance. In fact, the whole work appears to have been but partially finished, or constructed in great haste. The mounds at the gateways, and those outside of the walls, were formed by carelessly scooping up the earth at their base leaving irregular pits near them. In most of the regular works the material seems to have been taken up evenly and with care, or brought from a distance.
No one would be apt to ascribe a defensive origin to this work, yet it is difficult to conceive for what other purpose a structure of such dimensions, embracing nearly one hundred acres, could have been designed. The great mound is anomalous in its character, and throws no light on the question. That there is some hidden significance, in the first place in the regularity, and secondly in the arrangement of the various parts, can hardly be doubted. Nor can the coincidences observable between this and the other succeeding works of the same series be wholly accidental.43
42. Indicated by the letter K, in Map, Plate II.
43. To put, at once, all skepticism at rest, which might otherwise arise as to the regularity of these works, it should be stated that they were all carefully surveyed by the authors in person. Of course, no difficulty existed in determining the perfect regularity of the squares. The method of procedure, in respect to the circles, was as follows. Flags were raised at regular and convenient intervals, upon the embankments, representing stations. The compass was then placed alternately at these stations, and the bearing of the flag next beyond ascertained. If the angles thus determined proved to be coincident, the regularity of the work was placed beyond doubt. The supplementary plan A indicates the method of survey, the "Field Book" of which, the circle being thirty-six hundred feet in circumference, and the stations three hundred feet apart. is as follows:
| STATION. | BEARING. | DISTANCE. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | N. 75° E. | 300 feet. |
| 2 | N. 45° E. | 300 feet. |
| 3 | N. 15° E. | 300 feet. |
| 4 | N. 15° W. | 300 feet. |
| 5 | N. 45° W. | 300 feet. |
| 6 | N. 75° W. | 300 feet. |
| 7 | S. 75° W. | 300 feet. |
| 8 | S. 45° W. | 300 feet. |
| 9 | S. 15° W. | 300 feet. |
| 10 | S. 15° E. | 300 feet. |
| 11 | S. 45° E. | 300 feet. |
| 12 | S. 75° E. | 300 feet. |

